
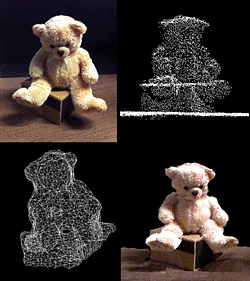
When the ArKinect scans an object, it collects surface and depth data, then combines them into a 3-D rendering. (Lynn Welton, Courtesy California Institute for Telecommunications and Information Technology)
A technological marriage between archaeology and video gaming may beget crisp, 3-D virtual renderings from ancient excavation sites that will one day help archaeologists better track the progression of digs, record the locations of artifacts, and even beam images to remote researchers who can consult on fieldwork.
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD), hacked a Microsoft Xbox 360 Kinect to create a low-cost 3-D scanner that can be used in the field. Ordinarily, the Kinect peripheral tracks the motion of game players by following infrared dots it projects onto them, allowing online avatars in games to be controlled by movement alone—no controller required. The UCSD team turned the device into a hand-held scanner that, when passed over every inch of an area or object (researchers liken the process to spray painting), can collect depth, surface texture, and color data. This information can then be combined to create a virtual representation of an artifact or a dig site.
Currently the ArKinect, as it's called, requires a separate video tracking system that allows users to properly orient the scanner. The researchers, however, hope to have an untethered prototype that they can use in the field on an upcoming dig in Jordan. The ArKinect offers a far cheaper, more portable alternative for creating 3-D renderings than light detection and ranging (LiDAR), which, because of the system's size, isn't as flexible for capturing all the contours of a large site or artifact.
Advertisement

Advertisement







